MD5 vs SHA-256 password hashing
Task: Comparing MD5 and SHA‑2 for Password Hashing
Presented at a research symposium in April 2022
Password hashing is a fundamental part of secure authentication systems but not all hashing algorithms are created equal. In this presentation, I explored and compared MD5 and SHA‑2 in terms of performance, security, and suitability for password storage.
Why It Matters
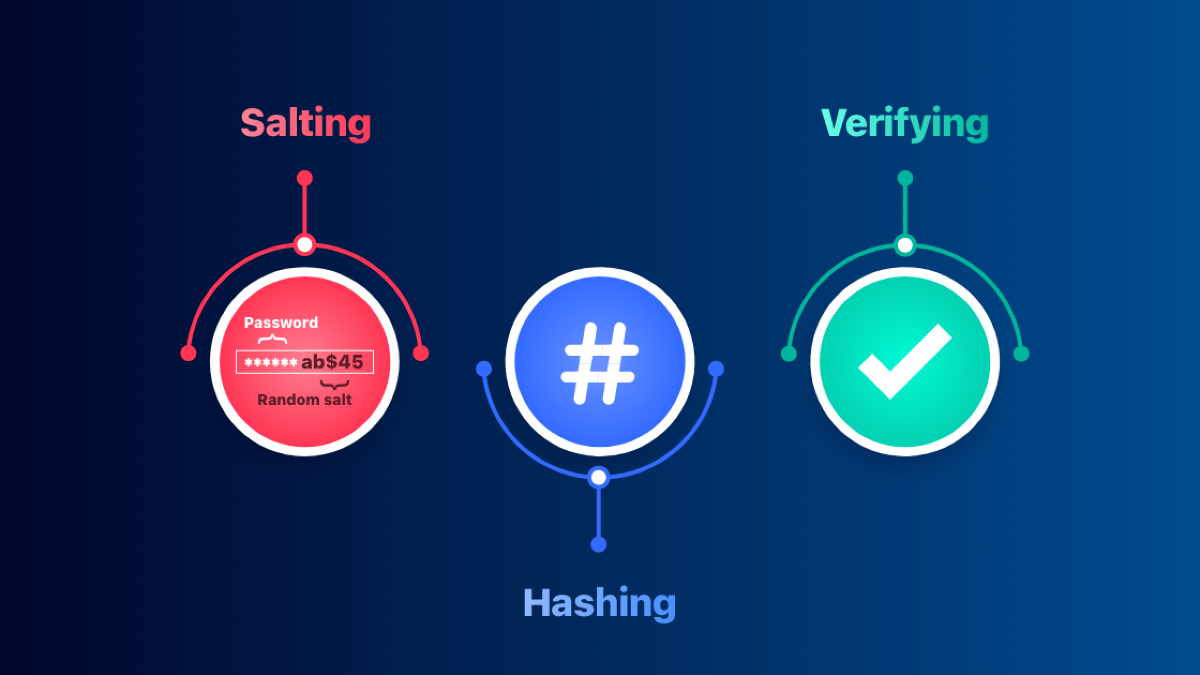
Hash functions convert passwords into fixed-size, irreversible values so that even if a system is breached, plaintext passwords remain unrecoverable. However, as hashing speed increased, so did the effectiveness of attacks like collisions and brute-forcing. At the same time, modern guidelines have shifted toward slower, more robust options like SHA‑2 and even more advanced schemes like bcrypt or Argon2.
Evaluation Criteria
I assessed the two algorithms using:
- - Collision resistance
- - Hash and digest length complexity
- - Processing speed and computational overhead
- - Practical security when used to hash passwords
My research showed that although MD5 performs faster ( about 20% quicker), it fails to meet current security standards. MD5’s vulnerability to collision attacks and rainbow tables makes it unsuitable for password storage. Meanwhile, SHA‑2 particularly SHA‑256 struck a much better balance between performance and protection
Key Conclusions
- - MD5 is obsolete for password hashing due to its cryptographic weaknesses even when salted.
- - SHA‑2 is a more secure alternative and remains widely adopted, though best practices now lean toward adaptive algorithms with built-in resistance to brute‑force attacks (e.g., bcrypt, scrypt, Argon2).
- - Layered security matters: strong hash functions should be part of a broader strategy that includes salting, multi-factor authentication, and identity management controls.
Professional Takeaway
This project sharpened my understanding of cryptographic principles, algorithm selection, and evolving security standards. It reinforced the importance of ongoing evaluation and adapting to modern threats especially when legacy methods no longer suffice.
🔗 View the presentation details and poster: Comparing MD5 and SHA‑2 in password hashing (April 2022)